本实验室青年教师科研成果在国际著名期刊nature communications 发表
时间:2016-9-13 作者:admin
近日,本实验室青年教师朱本亮联合德国奥尔登堡大学张彦振博士,在国际著名学术期刊nature communications(影响因子11.329)上发表科研成果《Hydrodynamic dispensing and electrical manipulation of attolitre droplets》。Nature及其系列子刊等相关出版物均具有极高的影响因子,是自然基础科学各学科领域的核心刊物。
论文运用大量实验,提出一种全新的吸入式微纳尺度液滴产生方法,揭示了该方法的内在机理,并结合电场提出了微纳液滴的操作方法。此方法不仅可以得到远小于管口直径大小的液滴,且可以处理大粘度(高达几千毫帕)流体,大幅提升了的受控液体种类。该方法在生物检测、化学分析和微表面加工装饰等领域有着极为重要的应用前景。Paper name:
Hydrodynamic dispensing and electrical manipulation of attolitre droplets
Abstract:
Dispensing and manipulation of small droplets is important in bioassays, chemical analysis and patterning of functional inks. So far, dispensing of small droplets has been achieved by squeezing the liquid out of a small orifice similar in size to the droplets. Here we report that instead of squeezing the liquid out, small droplets can also be dispensed advantageously from large orifices by draining the liquid out of a drop suspended from a nozzle. The droplet volume is adjustable from attolitre to microlitre. More importantly, the method can handle suspensions and liquids with viscosities as high as thousands mPa s markedly increasing the range of applicable liquids for controlled dispensing. Furthermore, the movement of the dispensed droplets is controllable by the direction and the strength of an electric field potentially allowing the use of the droplet for extracting analytes from small sample volume or placing a droplet onto a pre-patterned surface.
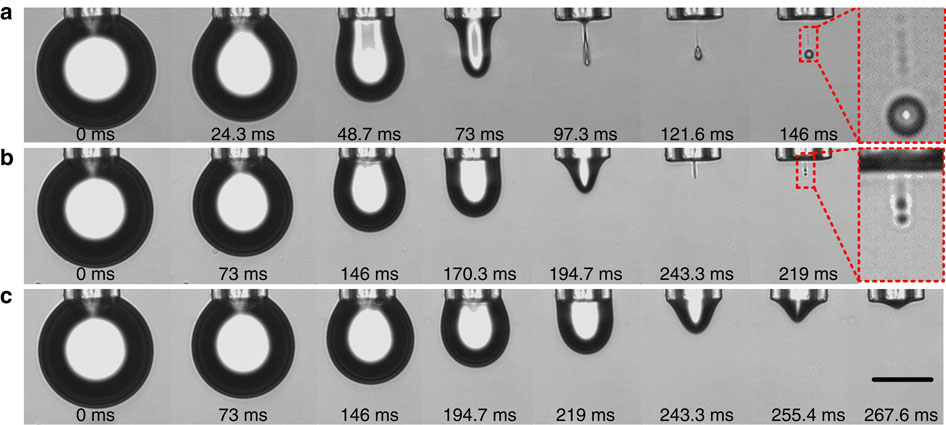
Figure 1 Three regimes of droplet formation

Figure 2 Dispensed droplets and microcapsules





